Discovery of Rocks Indicating Ancient Water Flows on Mars thanks to the Perseverance Rover
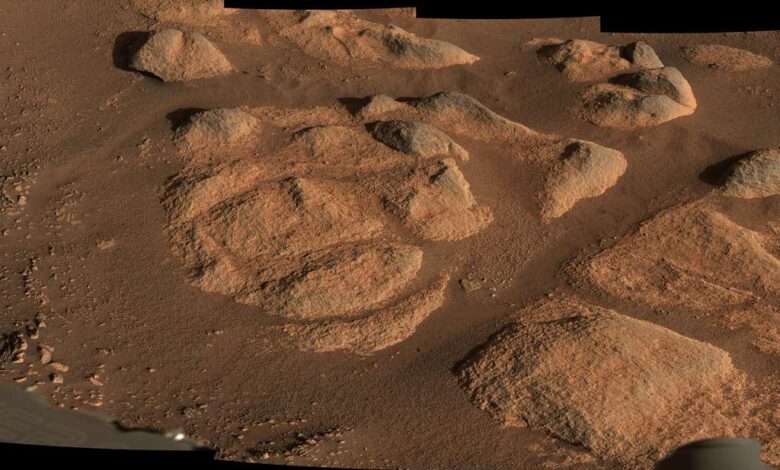

An international research team, involving several French laboratories, has made a significant discovery thanks to NASA’s Perseverance rover, which is exploring the planet Mars. The detection of rocks exhibiting signs of ancient water circulation on the Martian surface is a remarkable finding.
The French National Center for Scientific Research (CNRS), which contributed to this discovery, stated in a press release that while quartz is common in Earth’s crust, this marks the first time that this mineral has been directly identified on the surface of the red planet. This discovery was recently published in the specialized journal Earth and Planetary Science Letters.
The detected rocks provide evidence of “very ancient water circulation on Mars” and are of particular interest from an astrobiological perspective, according to the CNRS.
The research center explains that siliceous rocks, especially opal, possess exceptional properties for preserving traces of life, whether morphological or molecular. If the Perseverance rover succeeds in sampling these types of rocks, they will become prime targets for searching for signs of life once they are returned to Earth.